Discover how autonomous vehicles are revolutionizing the world of freight transportation in this insightful blog post on “The Dawn of a New Era: Autonomous Vehicles in the World of Freight Transportation.”
Delve into the transformative impact of digital freight forwarding, enhancing freight transportation security, the role of freight brokerage, last-mile delivery advancements, and the evolving landscape of freight logistics.
Uncover the potential of autonomous vehicles in streamlining sea freight and air freight operations, while empowering freight forwarders to adapt to a new era of innovation. Stay ahead of the curve with this captivating exploration of autonomous vehicles shaping the future of the freight transportation industry.
- Introduction to Autonomous Vehicles in the World Of Freight Transportation
- 1. Digital Freight Forwarding: Embracing the Technological Wave
- 2. Enhancing Freight Transportation Security: Safeguarding the Future
- 3. Freight Brokerage: Navigating the New Frontier
- 4. Last-Mile Delivery: Bringing Innovation to Your Doorstep
- 5. Freight Logistics: Paving the Way for Efficiency
- 6. Freight Forwarders: Embracing Innovation for Success
- Benefits of Autonomous Vehicles in The World Of Freight Transportation
- Safety and Regulatory Considerations in the World of Freight Transportation
- Impact on the Workforce and Job Market in the World of Freight Transportation
- Infrastructure and Integration Challenges in the World of Freight Transportation
- Future Outlook and Emerging Trends in the World of Freight Transportation
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Related Articles
Introduction to Autonomous Vehicles in the World Of Freight Transportation
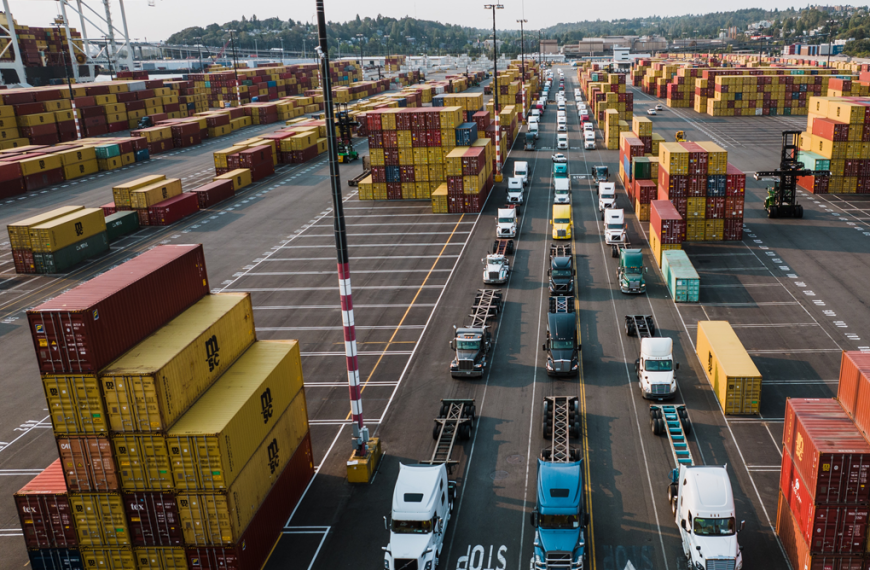
The world of freight transportation is on the cusp of a monumental shift—a new era driven by the emergence of autonomous vehicles. Imagine a future where the movement of goods is no longer bound by traditional limitations. Autonomous vehicles are poised to disrupt the industry, revolutionizing the way we think about digital freight forwarding, freight transportation security, freight brokerage, last-mile delivery, freight logistics, and the pivotal role of freight forwarders.
1. Digital Freight Forwarding: Embracing the Technological Wave
In this era of digital transformation, the concept of freight forwarding has evolved. Digital freight forwarding leverages cutting-edge technologies to streamline processes, enhance efficiency, and improve overall visibility in the supply chain. By seamlessly integrating autonomous vehicles into this landscape, the industry gains an unprecedented level of control and agility.
2. Enhancing Freight Transportation Security: Safeguarding the Future
Freight transportation security is a paramount concern, and autonomous vehicles have the potential to address it head-on. With advanced sensors, real-time tracking capabilities, and robust encryption protocols, these vehicles can bolster security measures and mitigate risks associated with cargo theft, unauthorized access, and tampering.
3. Freight Brokerage: Navigating the New Frontier
As the backbone of the industry, freight brokerage plays a pivotal role in connecting shippers and carriers. The rise of autonomous vehicles opens up new possibilities for freight brokers, enabling them to optimize routes, reduce costs, and facilitate seamless transactions. By harnessing the power of automation and data analytics, brokers can make smarter decisions in a dynamic and evolving landscape.
4. Last-Mile Delivery: Bringing Innovation to Your Doorstep
The final leg of the delivery journey, last-mile delivery, presents unique challenges that autonomous vehicles can help overcome. From small parcels to large shipments, self-driving trucks and drones can navigate congested urban areas, ensuring swift and efficient deliveries. This transformative capability promises faster turnaround times, reduced carbon emissions, and increased customer satisfaction.
5. Freight Logistics: Paving the Way for Efficiency
Efficient freight logistics is the backbone of a thriving supply chain ecosystem. Autonomous vehicles offer a paradigm shift, enabling seamless integration across modes of transport, optimizing route planning, and minimizing idle time. Whether it’s sea freight, air freight, or road transportation, the autonomous revolution holds the key to unlocking new levels of efficiency and reliability.
6. Freight Forwarders: Embracing Innovation for Success
Freight forwarders are the driving force behind international trade, and embracing autonomous vehicles is essential for their continued success. By leveraging self-driving technology, freight forwarders can enhance their operations, improve lead times, reduce costs, and deliver exceptional value to their clients. This new era demands adaptability and a proactive approach to stay ahead of the competition.
In this blog series, we will explore each facet of this groundbreaking transformation in detail. Join us as we dive deeper into the exciting world of autonomous vehicles in freight transportation, unearthing the challenges, opportunities, and endless possibilities that lie ahead.
Stay tuned for our next article on “Digital Freight Forwarding: Unlocking Efficiency in the Supply Chain.” Together, let’s embark on this journey into the future of freight transportation, where innovation meets possibility.

Benefits of Autonomous Vehicles in The World Of Freight Transportation
Autonomous vehicles are revolutionizing the world of freight transportation, bringing a multitude of benefits to businesses and the logistics industry as a whole. From digital freight forwarding to last-mile delivery, these vehicles are reshaping the way goods are moved and delivered, enhancing efficiency, and ensuring secure and reliable transport. Let’s delve into the remarkable advantages they offer:
| Benefits | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Efficiency | Autonomous vehicles optimize the freight transportation process, selecting the most efficient routes, avoiding traffic congestion, and reducing delivery delays. These vehicles leverage real-time data analysis and advanced algorithms to streamline operations and deliver goods faster and more reliably. |
| Cost Reduction | By eliminating the need for rest breaks and human limitations, autonomous vehicles operate around the clock, significantly reducing labor costs. Moreover, they optimize fuel consumption, enhance resource allocation, and minimize maintenance expenses, resulting in substantial cost savings for businesses. |
| Improved Safety | Equipped with advanced sensors and artificial intelligence, autonomous vehicles detect and respond to potential risks on the road, minimizing human errors and accidents. This technology ensures a safer working environment for drivers and other road users, enhancing overall safety in freight transportation. |
| Streamlined Last-Mile Delivery | Last-mile delivery is made more efficient by autonomous vehicles. Self-driving trucks and drones navigate urban areas with precision, optimizing delivery routes, reducing transit times, and improving customer satisfaction. These vehicles contribute to a greener and more sustainable logistics ecosystem by reducing carbon emissions. |
| Optimal Resource Utilization | Autonomous vehicles leverage advanced analytics and interconnected systems to monitor and manage inventory levels, optimize cargo loading and unloading, and minimize idle time. This level of resource optimization leads to improved productivity, reduced wastage, and better utilization of available capacity. |
| Increased Flexibility and Scalability | With the ability to adapt to changing demands and dynamic supply chain requirements, autonomous vehicles provide businesses with greater flexibility and scalability. Whether adjusting routes, accommodating varying cargo sizes, or responding to market shifts, these vehicles empower businesses to scale operations efficiently. |
| Enhanced Customer Experience | Autonomous vehicles enhance the overall customer experience by providing faster and more reliable deliveries. With improved visibility throughout the transportation process, businesses can offer accurate tracking information, timely notifications, and seamless order fulfillment, leading to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty. |
These benefits demonstrate the transformative power of autonomous vehicles in the world of freight transportation. By embracing this technology, businesses can unlock new levels of efficiency, cost savings, safety, and customer satisfaction, setting the stage for a future where autonomous vehicles seamlessly integrate into the logistics landscape.
Safety and Regulatory Considerations in the World of Freight Transportation
Safety and regulatory compliance are critical aspects of the ever-evolving world of freight transportation. As the industry embraces technological advancements like digital freight forwarding, autonomous vehicles, and last-mile delivery innovations, it becomes paramount to address the safety implications and navigate the complex regulatory landscape. Let’s explore the key considerations that ensure safe and secure operations in this dynamic environment.
1. Development of Advanced Safety Systems: With the introduction of autonomous vehicles, the focus on safety reaches new heights. Cutting-edge technologies, such as advanced sensors, computer vision, and artificial intelligence, enable these vehicles to detect and respond to potential hazards in real time. Investments in the development and integration of robust safety systems are crucial to minimizing risks and ensuring the protection of cargo, drivers, and other road users.
2. Regulatory Challenges and Legal Frameworks: The rise of digital freight forwarding, autonomous vehicles, and innovative freight transportation methods raises a host of regulatory challenges. Governments and regulatory bodies must adapt their policies and establish clear guidelines to address safety standards, liability concerns, and operational requirements. Developing comprehensive legal frameworks that balance innovation, safety, and efficiency is essential to support the growth and integration of emerging technologies in the freight transportation industry.
3. Cybersecurity and Data Privacy: As the industry becomes increasingly digitized, safeguarding sensitive information and protecting against cyber threats is of paramount importance. Robust cybersecurity measures must be implemented to safeguard data related to digital freight forwarding, freight brokerage, and other freight logistics operations. Ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), is essential in maintaining the trust of customers and stakeholders.
4. Training and Skill Development: As technologies evolve, so must the skills and competencies of those working in the freight transportation industry. Ongoing training programs should be established to equip professionals with the necessary knowledge and expertise to operate and interact with advanced systems. Training should encompass not only the technical aspects of operating autonomous vehicles but also emphasize the importance of safety protocols, emergency response procedures, and compliance with regulatory guidelines.
5. Collaboration and Information Sharing: The complex nature of freight transportation necessitates collaboration among stakeholders, including freight forwarders, transportation companies, regulatory bodies, and technology providers. Sharing best practices, lessons learned, and safety data promotes a culture of continuous improvement and ensures a collective effort towards maintaining high safety standards. Open communication channels facilitate the exchange of knowledge and enable the industry to adapt and respond to evolving safety and regulatory requirements.
6. International Harmonization of Standards: As freight transportation operates on a global scale, harmonizing safety and regulatory standards is crucial. International collaboration is necessary to establish consistent guidelines, protocols, and standards that facilitate the seamless movement of goods across borders. Encouraging dialogue and cooperation between countries and regulatory bodies supports a unified approach to safety and regulatory compliance.
In this ever-changing landscape, prioritizing safety and navigating regulatory considerations are paramount in the world of freight transportation. By investing in advanced safety systems, fostering collaboration, and establishing robust legal frameworks, the industry can embrace innovation while ensuring the well-being of all stakeholders.
As technologies like digital freight forwarding and autonomous vehicles continue to shape the future, a proactive approach to safety and regulatory compliance is essential for a secure and thriving freight transportation ecosystem.

Impact on the Workforce and Job Market in the World of Freight Transportation
The evolving landscape of the freight transportation industry, driven by advancements such as digital freight forwarding, last-mile delivery innovations, and autonomous vehicles, is reshaping the workforce and job market. As technology continues to revolutionize operations in areas like freight transportation security, freight brokerage, and freight logistics, it’s essential to explore the impact on the workforce and the opportunities that arise. Let’s delve into the key factors shaping this transformation.
1. Automation and Job Displacement: The introduction of automation technologies, including autonomous vehicles and digital freight forwarding systems, has the potential to disrupt traditional roles within the industry.
While these innovations increase efficiency and streamline processes, certain job functions may become automated, leading to job displacement in specific areas such as repetitive manual tasks.
However, this shift also creates opportunities for upskilling and reskilling the workforce to take on new roles that leverage technology.
2. Evolving Skill Requirements: As the industry embraces digitalization and automation, the demand for workers with advanced technical skills increases.
Proficiency in data analysis, artificial intelligence, robotics, and cybersecurity becomes highly valuable in roles related to managing and optimizing autonomous vehicles, ensuring freight transportation security, and overseeing digital freight forwarding operations.
Upskilling programs and educational initiatives that equip workers with these skills will play a crucial role in meeting the evolving demands of the job market.
3. New Job Opportunities: While automation may displace certain roles, it also creates new job opportunities within the industry.
For instance, the implementation and maintenance of autonomous vehicles, as well as the management of complex digital freight forwarding systems, require skilled professionals to ensure their smooth operation.
Additionally, the rise of last-mile delivery solutions and the demand for efficient freight logistics open doors for new roles in logistics coordination, route optimization, and customer experience management.
4. Shift Towards Specialized Roles: As technology transforms the industry, there is a growing need for specialized roles that focus on areas such as freight transportation security, freight brokerage, and freight logistics optimization.
Professionals who can navigate regulatory requirements, ensure compliance, and develop innovative strategies for optimizing supply chains will be in high demand.
These specialized roles require a deep understanding of industry dynamics, emerging technologies, and the ability to adapt to changing market conditions.
5. Collaboration between Humans and Technology: Rather than replacing human workers entirely, the future of the workforce in freight transportation lies in collaboration with technology.
Autonomous vehicles and digital freight forwarding systems serve as powerful tools that augment human capabilities, enabling workers to focus on higher-level tasks that require critical thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making.
This collaboration creates a more efficient and productive work environment, allowing human workers to leverage their expertise while harnessing the benefits of automation.
6. Job Market Resilience: The continued growth and transformation of the freight transportation industry create a resilient job market.
While automation may reshape certain roles, it also stimulates the need for new skills and expertise. Adaptable workers who embrace lifelong learning and remain open to acquiring new skills will be well-positioned to navigate the evolving job market.
The ability to adapt to emerging technologies and trends, coupled with a strong foundation of industry knowledge, will be essential in seizing new opportunities as they arise.
In this era of rapid technological advancement, the workforce in the world of freight transportation must embrace change and adapt to the evolving job market.
As automation technologies like digital freight forwarding and autonomous vehicles reshape traditional roles, there is a growing need for workers with advanced technical skills, specialized knowledge, and the ability to collaborate effectively with technology.
By embracing upskilling initiatives and fostering a culture of continuous learning, the industry can ensure a resilient workforce that thrives in this exciting era of innovation.
Infrastructure and Integration Challenges in the World of Freight Transportation
In the rapidly evolving world of freight transportation, where digital freight forwarding, last-mile delivery innovations, and advanced technologies like autonomous vehicles are reshaping the landscape, infrastructure and integration challenges arise.
To fully harness the benefits of these advancements, it’s crucial to address the complexities and hurdles associated with infrastructure development and seamless integration. Let’s explore the key challenges that the industry faces in this regard.
1. Adaptation of Existing Infrastructure: The integration of emerging technologies requires adapting existing infrastructure to accommodate the changing needs of freight transportation.
For example, the deployment of autonomous vehicles necessitates infrastructure upgrades such as smart roadways, reliable communication networks, and charging or refueling stations.
Adapting existing infrastructure to support these innovations poses a considerable challenge, requiring collaboration between stakeholders, including government entities, transportation agencies, and technology providers.
2. Connectivity and Interoperability: Seamless integration of various systems and technologies is crucial for efficient freight transportation.
Achieving connectivity and interoperability between digital freight forwarding platforms, freight transportation security systems, and freight brokerage networks is essential for real-time data exchange, process optimization, and effective coordination.
However, different technologies and systems often operate in silos, creating challenges in achieving standardized connectivity and interoperability across the industry.
3. Data Management and Security: The advancements in digital freight forwarding and freight logistics generate vast amounts of data.
Efficient data management and robust cybersecurity measures are vital to ensure the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of this information.
Challenges include developing secure data exchange protocols, implementing data privacy regulations, and safeguarding against cyber threats.
Establishing industry-wide standards and frameworks for data management and security is crucial for building trust among stakeholders and protecting sensitive information.
4. Regulatory Frameworks and Standards: The integration of new technologies in freight transportation requires the establishment of clear regulatory frameworks and standards.
Addressing legal and regulatory challenges related to autonomous vehicles, last-mile delivery solutions, and digital freight forwarding is crucial for ensuring compliance, protecting the interests of all stakeholders, and fostering a level playing field.
Collaborative efforts between industry participants and regulatory bodies are necessary to develop and implement effective regulations that balance innovation, safety, and operational requirements.
5. Industry Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing: Overcoming infrastructure and integration challenges necessitates collaboration among various stakeholders, including freight forwarders, freight transportation companies, technology providers, and regulatory bodies.
Sharing knowledge, best practices, and lessons learned helps in identifying common challenges and developing innovative solutions. Industry associations, forums, and collaborative platforms play a vital role in facilitating such collaboration, enabling stakeholders to work together towards resolving infrastructure and integration hurdles.
6. Investment and Funding: The implementation of infrastructure upgrades and the integration of emerging technologies require significant investment.
Funding these initiatives poses challenges, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises. Public-private partnerships, government grants, and investment incentives can help bridge the financial gap and encourage industry-wide adoption of infrastructure upgrades and technology integration.
Collaboration between public and private sectors is crucial in securing the necessary funding to support the transformation of the freight transportation ecosystem.
Overcoming infrastructure and integration challenges is vital for unlocking the full potential of advancements like digital freight forwarding, last-mile delivery solutions, and autonomous vehicles.
By addressing adaptation needs, achieving connectivity and interoperability, establishing robust data management and security measures, developing effective regulatory frameworks, fostering industry collaboration, and securing adequate investment, the industry can navigate these challenges and build a resilient and integrated freight transportation ecosystem.
Together, stakeholders can pave the way for a future where technology and infrastructure work in harmony, enhancing efficiency, sustainability, and overall performance.

Future Outlook and Emerging Trends in the World of Freight Transportation
The world of freight transportation is on the cusp of a transformative era, driven by the rapid advancement of technologies like digital freight forwarding, last-mile delivery innovations, and automation. As the industry embraces these changes, it’s essential to explore the future outlook and emerging trends that will shape the landscape. Let’s delve into the exciting possibilities that lie ahead.
1. Digital Freight Forwarding Revolution: Digital freight forwarding is revolutionizing the way goods are transported globally. Leveraging cloud-based platforms, data analytics, and automation, it streamlines processes, enhances visibility, and optimizes supply chain efficiency.
The future will see further adoption of digital freight forwarding solutions, enabling seamless collaboration among freight forwarders, shippers, and carriers.
By harnessing the power of real-time data, artificial intelligence, and predictive analytics, businesses can make informed decisions and achieve cost savings while improving customer satisfaction.
2. Advancements in Freight Transportation Security: As the industry embraces digitalization and automation, there is a growing focus on freight transportation security.
Technologies like blockchain, Internet of Things (IoT), and machine learning are being leveraged to enhance cargo tracking, prevent theft, and mitigate risks.
Real-time monitoring, tamper-proof seals, and secure data exchange systems are just a few examples of emerging trends in freight transportation security. The future will witness increased adoption of these technologies, ensuring the integrity and safety of goods throughout the supply chain.
3. Last-Mile Delivery Innovations: Last-mile delivery, the final leg of the delivery process, is experiencing significant innovation.
E-commerce growth and changing consumer expectations are driving the need for faster, more flexible, and sustainable delivery options.
Emerging trends include the use of autonomous delivery robots, drones, and crowd-sourced delivery networks. These technologies promise to revolutionize last-mile logistics, reducing delivery times, optimizing routes, and minimizing carbon emissions.
4. Sustainable Freight Transportation: With a growing emphasis on sustainability, the future of freight transportation lies in greener and more environmentally friendly solutions.
Electric and hybrid vehicles, powered by renewable energy sources, are gaining traction in the industry. Additionally, there is an increased focus on optimizing transportation routes, reducing empty miles, and promoting multimodal transportation to minimize the carbon footprint of freight logistics.
Sustainable practices will not only benefit the environment but also improve operational efficiency and meet evolving customer expectations.
5. Integration of Autonomous Vehicles: Autonomous vehicles, including self-driving trucks and drones, hold immense potential in the freight transportation industry.
These vehicles offer increased efficiency, reduced labor costs, and improved safety. While full-scale implementation is still in the future, the industry is gradually witnessing the integration of autonomous features, such as driver-assist technologies and platooning.
As the technology matures and regulatory frameworks evolve, autonomous vehicles are set to revolutionize freight transportation, enabling longer operating hours, optimized fuel consumption, and improved overall productivity.
6. Enhanced Collaboration and Visibility: The future of freight transportation will be characterized by enhanced collaboration and visibility across the supply chain.
Emerging technologies like blockchain, IoT, and cloud-based platforms will facilitate seamless communication and data exchange between stakeholders, including freight forwarders, carriers, customs authorities, and customers.
Real-time tracking, end-to-end visibility, and transparent documentation will empower businesses to make faster, more informed decisions, improving operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
The future of the freight transportation industry is one of immense possibilities and exciting innovations. With the continued adoption of digital freight forwarding, advancements in freight transportation security, last-mile delivery innovations, sustainability initiatives, integration of autonomous vehicles, and enhanced collaboration across the supply chain, the industry is poised for remarkable growth.
Embracing these emerging trends will empower businesses to stay ahead of the curve, drive operational excellence, and deliver enhanced value to customers in the dynamic world of freight transportation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the examples of freight transport?
Freight transport encompasses various modes of transportation for the movement of goods. Examples include:
Trucking: The most common mode, involving the use of trucks to transport goods on roads and highways.
Railway: Utilizing trains to transport freight over long distances, especially for heavy and bulk cargo.
Maritime: Shipping goods by sea using cargo ships, containers, and vessels for international trade and large-scale shipments.
Air Cargo: Transporting goods by air through dedicated cargo planes, ideal for time-sensitive and high-value shipments.
Pipelines: Specialized mode for transporting liquids and gases over long distances, mainly for oil, gas, and water.
What are the five 5 major modes of freight transportation?
The five major modes of freight transportation are:
Trucking: Involves the use of trucks for door-to-door delivery, offering flexibility and extensive coverage.
Railway: Utilizes trains to transport large quantities of goods over long distances efficiently.
Maritime: Involves shipping goods through oceans and seas using cargo ships and containers, suitable for international trade and bulk shipments.
Air Cargo: Provides fast and reliable transportation for time-sensitive and high-value goods, often used for express deliveries.
Pipelines: Specialized mode for transporting liquids and gases through dedicated pipelines, primarily used for oil, gas, and water distribution.